Clean Room and Classification: Summary of 4 Different Standards

The area where the lowest concentration of air-borne particles is controlled is called a clean room. Clean room classification depends on various air-borne particles present in the respective area.
The degree of cleanliness of a clean room is measured in terms of the number of particles per m3 or ft3 for specific particle size.
In life sciences and healthcare, maintaining cleanrooms is critical since airborne contaminants can compromise product quality. To prevent contamination, industries adhere to strict cleanroom standards to ensure products remain pure and high-quality.
This means manufacturing areas must minimize particle presence to the greatest extent possible.
To achieve this, we must control:
- The environment
- Movement within the environment
Let’s dive into how both factors can be effectively controlled.
Table of Content
1. Environment
Air acts as a carrier for micro-organisms.
For a controlled environment, it is important to ensure the air entering the manufacturing area have the lowest particle count.
To achieve this, HEPA and ULPA filters are used.
| Term | Full Form | Pore Size (microns) |
|---|---|---|
| HEPA | High-Efficiency Particulate Air | 0.25 to 0.30 or larger |
| ULPA | Ultra Low Particulate Air | 0.12 to 0.13 or larger |
A ULPA filter is used for tighter requirements than a HEPA filter.
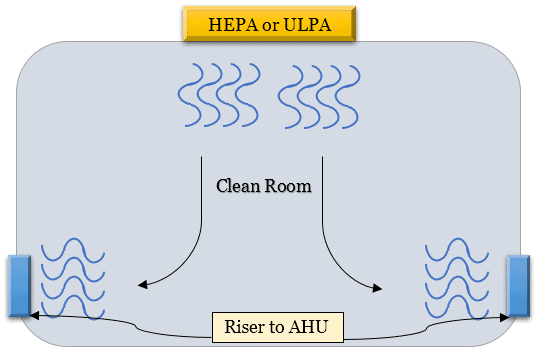
These filters are a key component of the HVAC system.
And they’re located on the false ceiling so that the fresh air comes into the room from the top and leaves through the risers installed at the bottom.
In addition to this, below parameters also helps to achieve a controlled environment:
- Temperature
- Relative Humidity
- Differential Pressure
2. Movement In The Environment
Once the environment is controlled, the next thing is to control the movement in the environment e.g. process and personnel movement.
A person entering the controlled area carries foreign particles with the body. The same is the case for raw materials and tools.
Being a potential source of contamination, people working in a clean environment require proper training and practice.
To avoid contamination caused by movement in the environment, the following checkpoints shall be considered.
- SOPs
- Personnel Entry and Exit Procedure
- Material Entry and Exit Procedure
- A list displayed outside the controlled area for the personnel allowed to enter
- Personnel Hygiene Practices
- Good Manufacturing Practices, etc.
- Ready to use sterilized gowns (lint-free)
- Head Caps, Beard Masks, Gloves, Hand Sanitizer, Goggles, Booties, Masks, etc.
- Providing and promoting the use of air showers.
It is essential to ensure the end products are of high quality. But before that, it is essential to ensure the operations being performed in a controlled environment are of high quality.
Let’s take a look at the different classifications of the clearooms.
Clean Room and Classification
Clean rooms are classified considering the particle size ≥ 0.5 microns per m3 or ft3.
Major cleanroom standards are:
- United States: FED STD 209E: Federal Standard 209E
- United Kingdom: British Standards BS 5295
- International Organization for Standardization: ISO 14644-1
- Europe: European Union Standard (European Economic Commission (EEC))
Let’s see one by one.
FED STD 209E (FEDeral STandarD)
The United States General Services Administration canceled this standard in November 2001, switching it with ISO standards.
Nonetheless, the standard is sometimes taken into consideration, particularly to relate with ISO standards.
According to FED STD 209E, the cleanroom classification is:
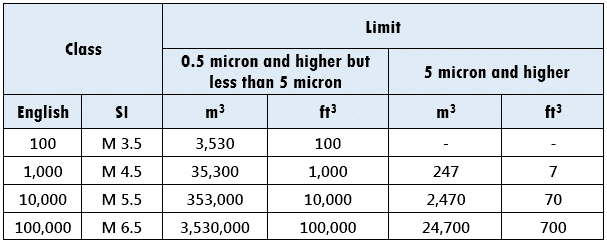
Meaning:
For a Class 100,000 area (1 Lakh), for particle size range 0.5 to <5 microns, maximum particle count must not exceed 100,000 particles per ft3 OR 3,530,000 particles per m3.
Likewise, for the same class, for particle size >/= 5 microns, maximum particle count must not exceed 700 particles per ft3 OR 24,700 particles per m3.
BS 5295 (British Standard)
The BSI offers the BS 5295 standard to specify the clean rooms and their classification. In order to classify clean rooms, they divided them into 10 categories.
Anyways, just like FED STD 209E, BS 5295 is superseded by ISO 14644-1.
ISO 14644-1 (International Organization for Standardization)
According to ISO, the area is categorized into nine classes. As the ISO number decreases, the number of particles in the air decreases.
Here is the table.
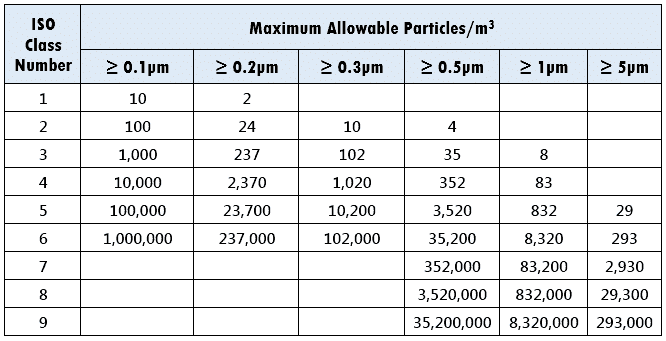
You can interprete these values just like we did above for US FED STD 209E.
The closest formula that fits the above values is:
Cn = 10N * (0.1/D)2
where,
N – ISO Class number
D – Diameter of the particle, or size of the particle
Cn – Maximum concentration (Particles per m3)
European Union Standard
To make you aware of the fact:
1993 marked the incorporation of the EEC (European Economic Community) into the European Union (EU), and became the European Community (EC). The EC lost its existence as of 2009, and the EU absorbed its institutions directly. Consequently, the EU became the successor organization to the EC.
The EU guidelines are tighter than US FED STD 209E and laid down clean room and classification based on two conditions:
- At Rest – No personnel in clean room and all equipment are idle. Thus, dispersion of air borne particles is about nill.
- In Operation – Running equipment with personnel presence.
EEC uses the term “Grade” instead of “Class”:
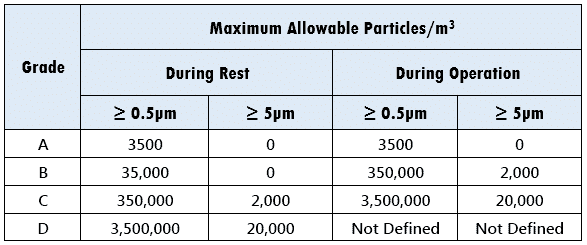
As you can see, Grade A requirements are more stringent due to the laminar airflow profile. Additionally, particles ≥ 5 microns are not acceptable both during rest and operation.
Summarizing the EU standard:
- Final product packaging and processing are done in the Grade A area.
- Final product loading and unloading are done in the Grade B area.
- Downstream Process operations performed in Grade D followed by Grade C area.
The above EU values too are obsolete now.
Because the EU GGMP Annexure-1 that specifies the environmental conditions to manufacture parenteral products, now requires the classification of different cleanroom grades and zones consistent with ISO 14644-1.
ISO 14644-1: 2015 standards refers to the cleanrooms and clean zones.
Whereas, EU GGMP’s Annexure 1 (2008) refers to the cleanrooms and clean air devices.
Equivalence Between EU and FED STD 209E
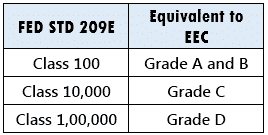
FAQs:
How are clean rooms classified?
Different standards have classified cleanrooms such as: United States: FED STD 209E: Federal Standard 209E, United Kingdom: British Standards BS 5295, International Standards Organization ISO 14644-1, Europe: European Economic Commission. The cleanrooms are classified based on the number of maximum allowable particles per cubic meter.
What is first air in clean room?
Fresh air entering the cleanroom from the HEPA filter is considered particulate-free and as first air.
What is the meaning of clean room?
An environment involving lower levels of contaminants, air-borne particulates, dust, bacteria, and other micro-organisms may affect the quality of the drug product when it comes in contact. Different regulations outline these low-level requirements for healthcare facilities, including pharmaceuticals, laboratories, etc.
What is a Class 1000 clean room?
Class 1000 of US FED STD 209E i.e., ISO 14644-1 Class 6 represents the requirement for maximum allowable particles as 35,200 (No. of particles/m3) when the size of the particle is greater or equivalent to 0.5 microns and less than 5 microns.
What is a Class 7 clean room?
ISO 14644-1 Class 7 i.e. US FED STD 209E Class 10,000 represents the requirement for maximum allowable particles as 3,52,000 (No. of particles/m3) when the size of the particle is greater or equivalent to 0.5 microns and less than 1 micron.
What is a Class 8 clean room?
ISO 14644-1 Class 8 i.e., US FED STD 209E Class 1,00,000 represents the requirement for maximum allowable particles as 35,20,000 (No. of particles/m3) when the size of the particle is greater or equivalent to 0.5 microns and less than 1 micron.
What is a Class 1 clean room?
Clean room becomes less stringent with the increasing number of classes such as Class 1 representing the cleanest room while Class 9 being the dirtiest.
Conclusion
In short, cleanroom classifications evolve with regulations—but their core objective remains the same: maintaining clean air and eliminating contaminants.
Before implementing different cleanroom classes, make sure to:
✔ Interpret regulatory requirements correctly
✔ Align operations to meet compliance standards
✔ Optimize airflow to control contamination effectively
This article provides an overview of current cleanroom classification regulations.
If you’re interested in how cleanrooms are designed, check out our guide on HVAC system design for pharmaceutical industries.
Have thoughts to share? Drop a quick comment below!






Excellently put. Easy to understand.
Very well defined about classification and easy to understand. Thank you very much for valuable information.
Hey Dangeti! Glad you find this valuable.
Very clear definition and very well defined. It was a easy read and got good knowledge.
Glad you liked it, Vikash 🙂
I have got a primary idea about Cleanroom and its classification. The clarity in the write-up is very much appreciating!!!
Thanks Nurul! Appreciate your words 🙂
Thanks for valuable information sir
Glad you found this valuable 🙂